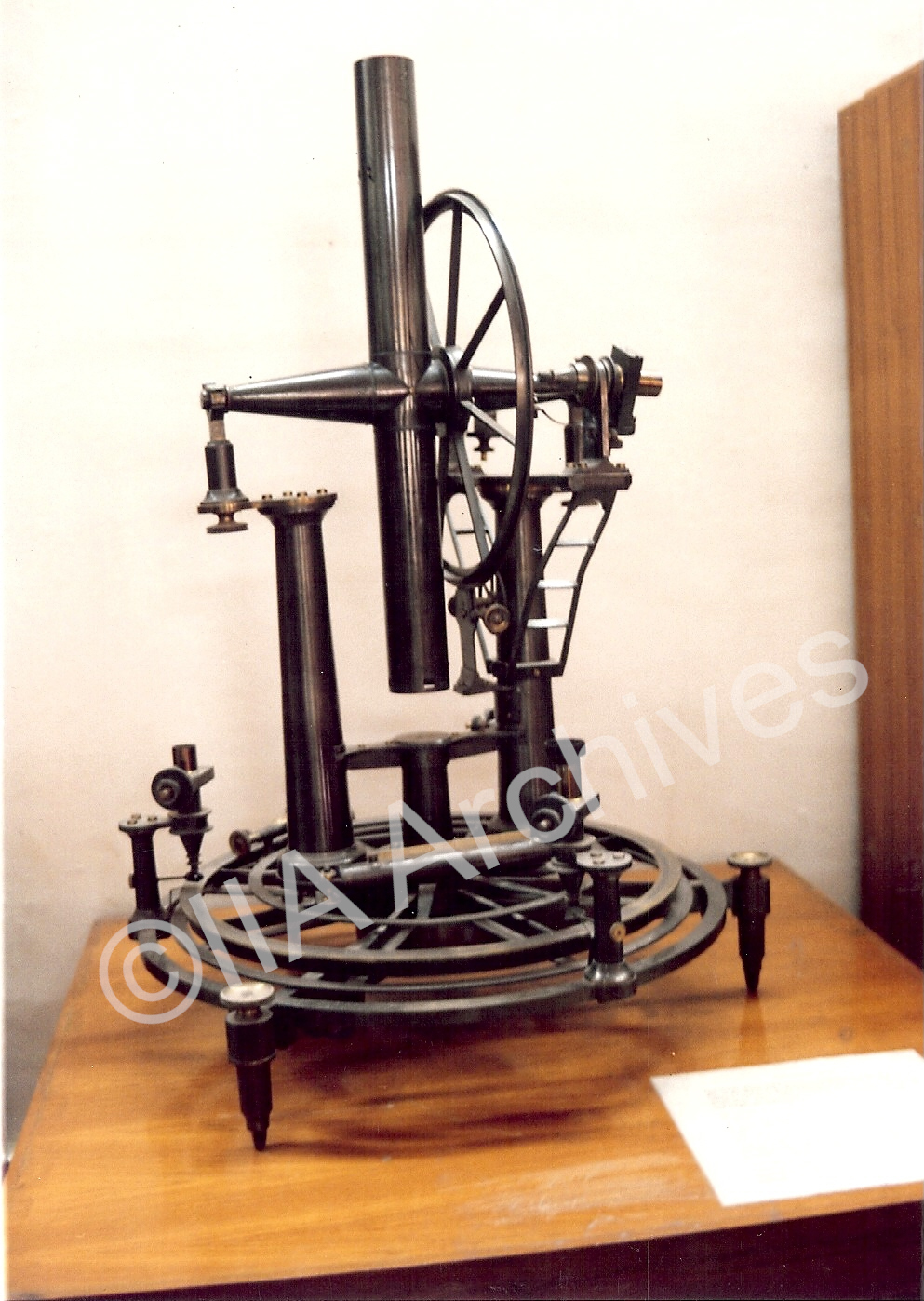
 Transit Circle (designed by Sir George Airy, 1850): The position of an astronomical object is given by two coordinates: Right Ascension and Declination. This is similar to the two coordinates, latitude and longitude, that determine the location on the surface of the Earth. Transit Circle (designed by Sir George Airy, 1850): The position of an astronomical object is given by two coordinates: Right Ascension and Declination. This is similar to the two coordinates, latitude and longitude, that determine the location on the surface of the Earth. | 
Theodolite (around 1850): A theodolite is a refracting telescope that can rotate in horizontal and vertical axes and provide angular readouts. It can measure tilt angles with very high accuracy of the order of arcseconds. It is used mainly in land surveying and in alignment, testing, and calibration of optical instruments. |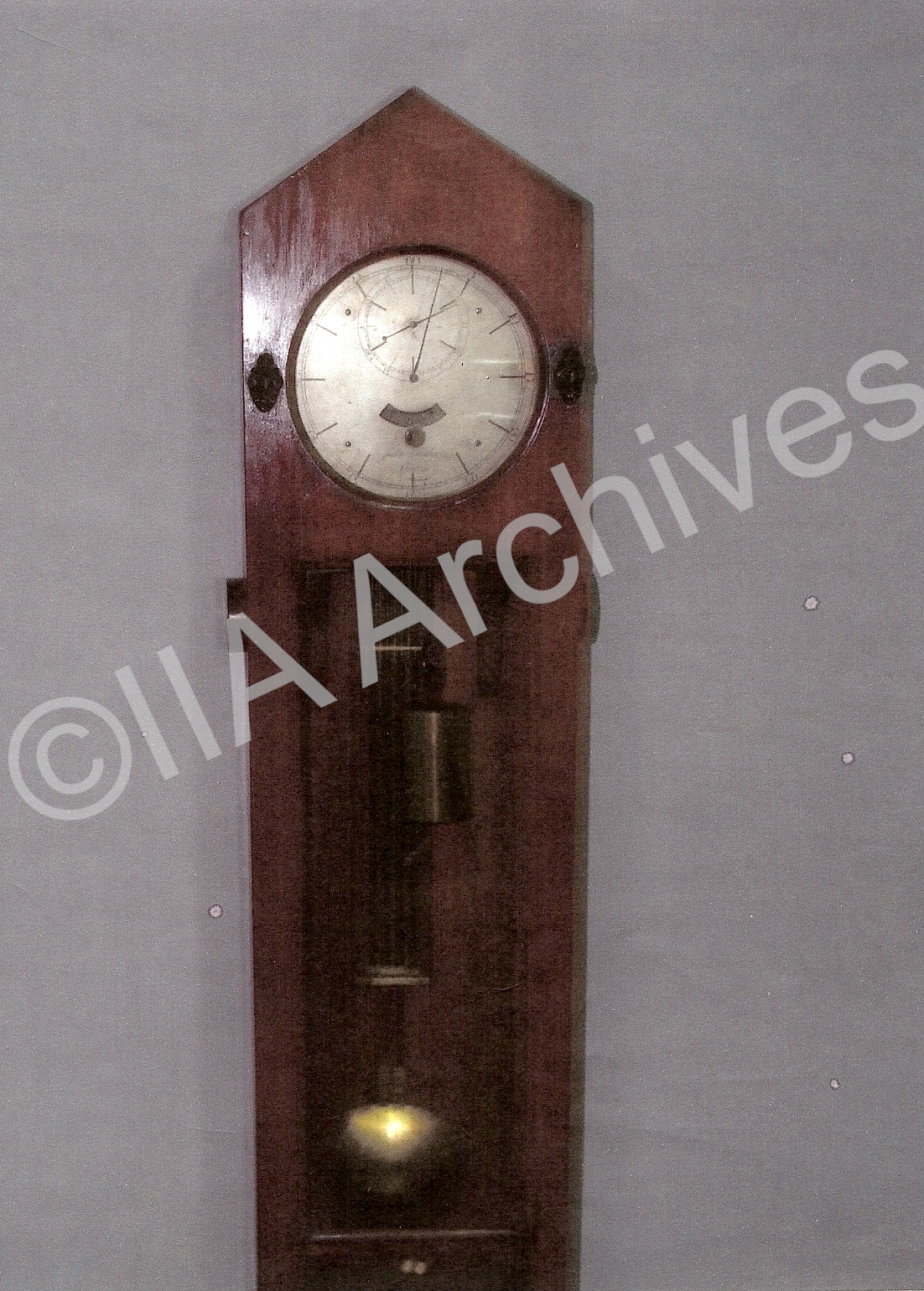 
Shelton Clock: This is a pendulum clock used at the Madras Observatory manufactured sometimes in 1786. It is presently kept at Kodaikanal field station and is in good working conditions. |
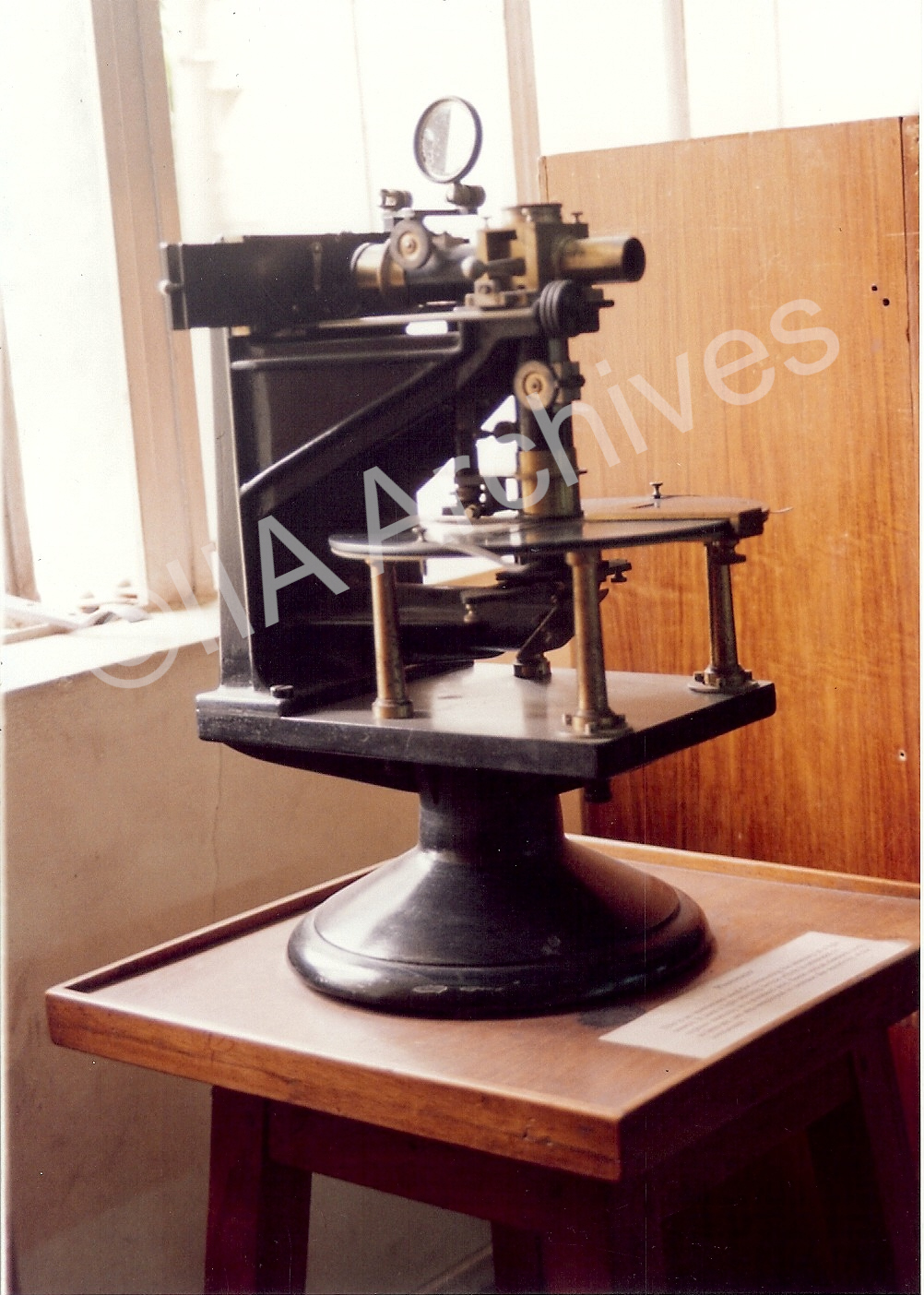 Photometer (designed by Dr. Hartmann, 1912): A photometer is used for measuring the intensity of a light source. It uses a light-sensing device that is calibrated to express the intensity in a standard unit. Depending on the sensor used, the incident light can cause a change in voltage, resistance, or current. Photometer (designed by Dr. Hartmann, 1912): A photometer is used for measuring the intensity of a light source. It uses a light-sensing device that is calibrated to express the intensity in a standard unit. Depending on the sensor used, the incident light can cause a change in voltage, resistance, or current. |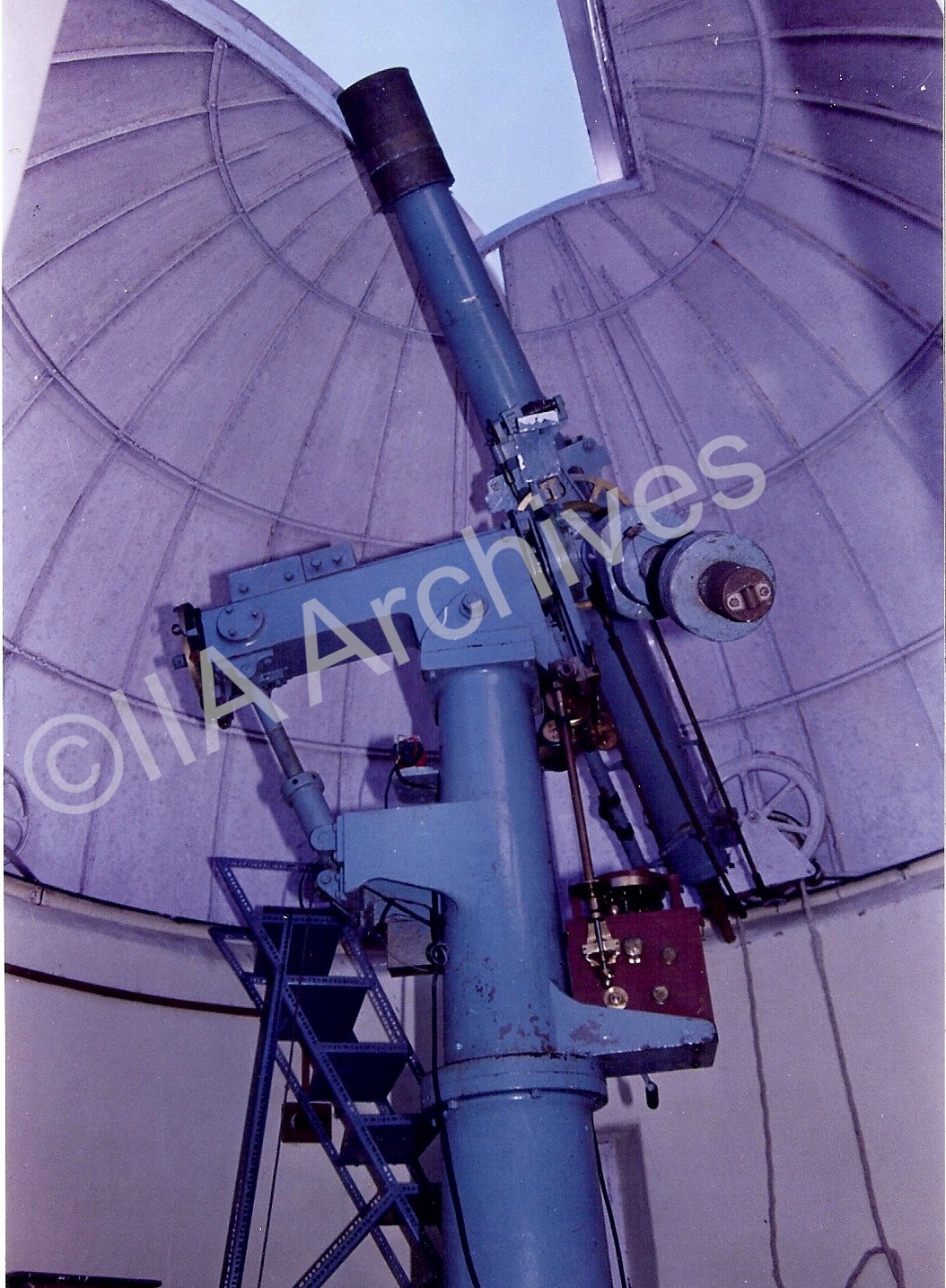  Six-inch equatorial manufactured by Lereboursand: A 6-inch telescope manufactured by Lerebours & Secretan of Paris, France, mounted on an English mounting, acquired in 1850 by the Madras Observatory is installed in the north dome at Kodaikanal Observatory. Six-inch equatorial manufactured by Lereboursand: A 6-inch telescope manufactured by Lerebours & Secretan of Paris, France, mounted on an English mounting, acquired in 1850 by the Madras Observatory is installed in the north dome at Kodaikanal Observatory. |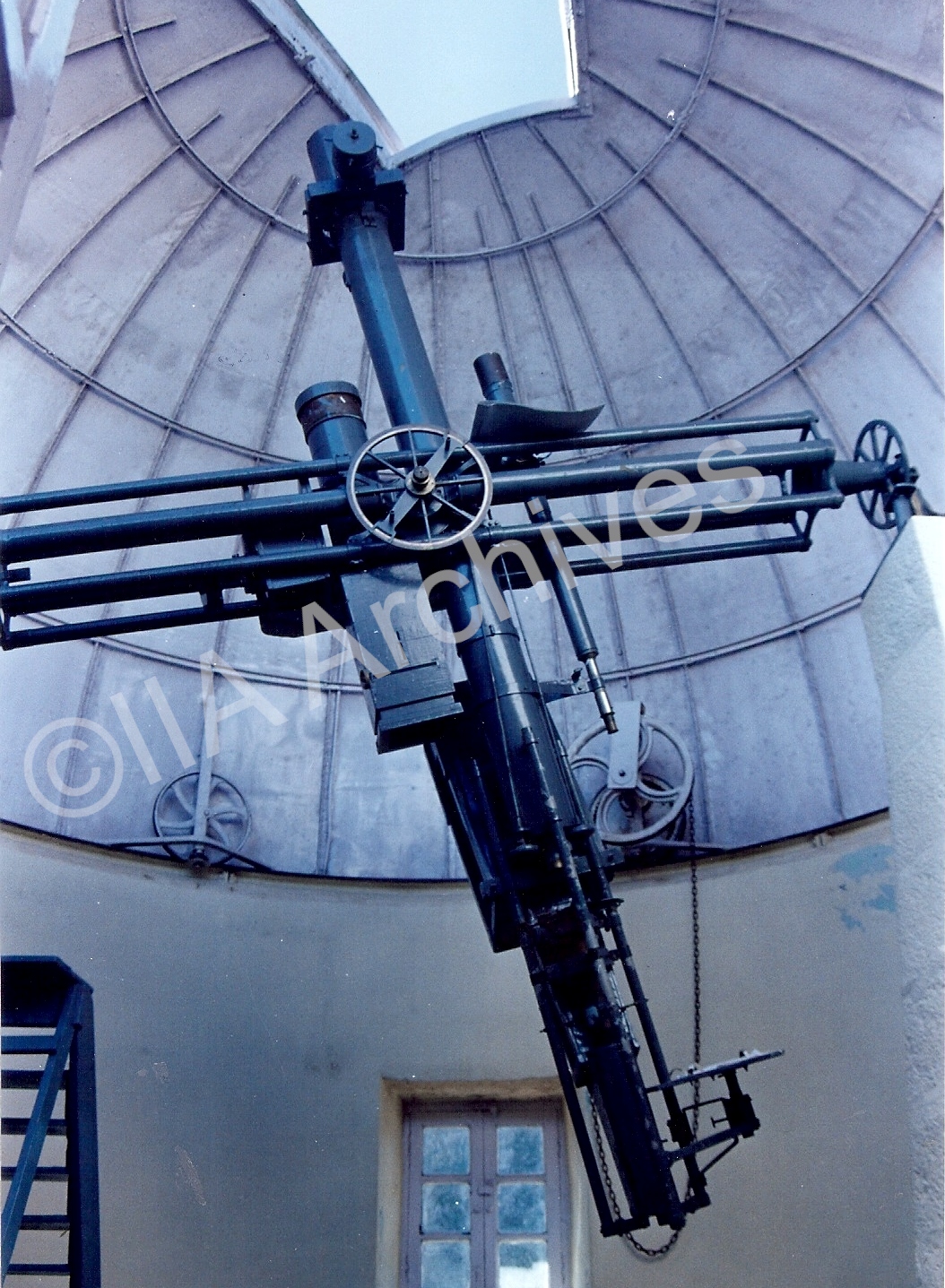  Eight-inch equatorial by Troughton and Simms (1864) was used for several observations by N. R. Pogson. The discovery of the asteroid Sylvia was made with this telescope. It was sent to Kodaikanal in 1931 and was mounted in the South Dome in 1960 by Prof. M. K. Vainu Bappu. This was used for several stellar observations for many years. Eight-inch equatorial by Troughton and Simms (1864) was used for several observations by N. R. Pogson. The discovery of the asteroid Sylvia was made with this telescope. It was sent to Kodaikanal in 1931 and was mounted in the South Dome in 1960 by Prof. M. K. Vainu Bappu. This was used for several stellar observations for many years. |
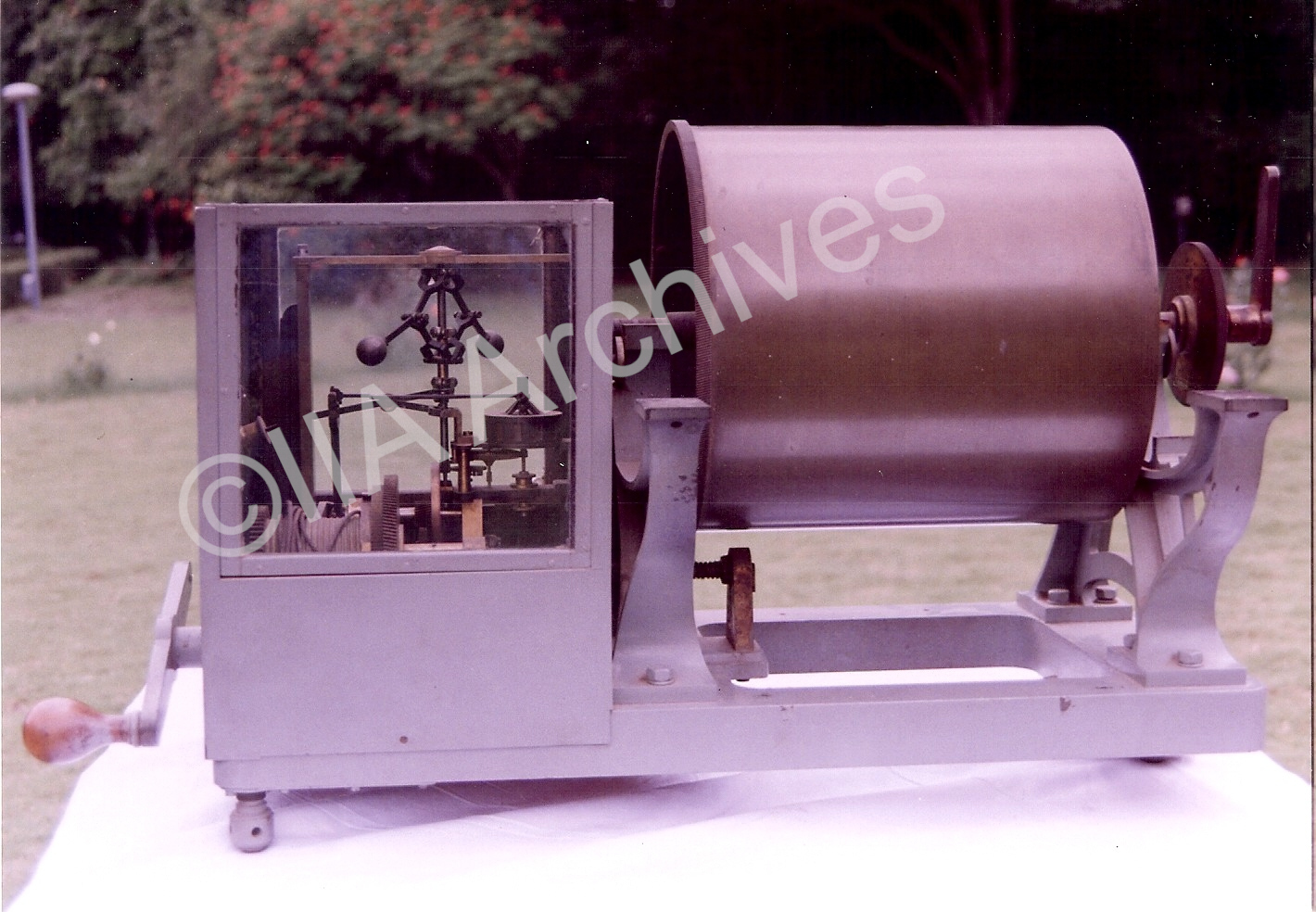

Drum Chronograph (designed by Eicheus & Hadly in 1872): A chronograph is an instrument to measure time very accurately. |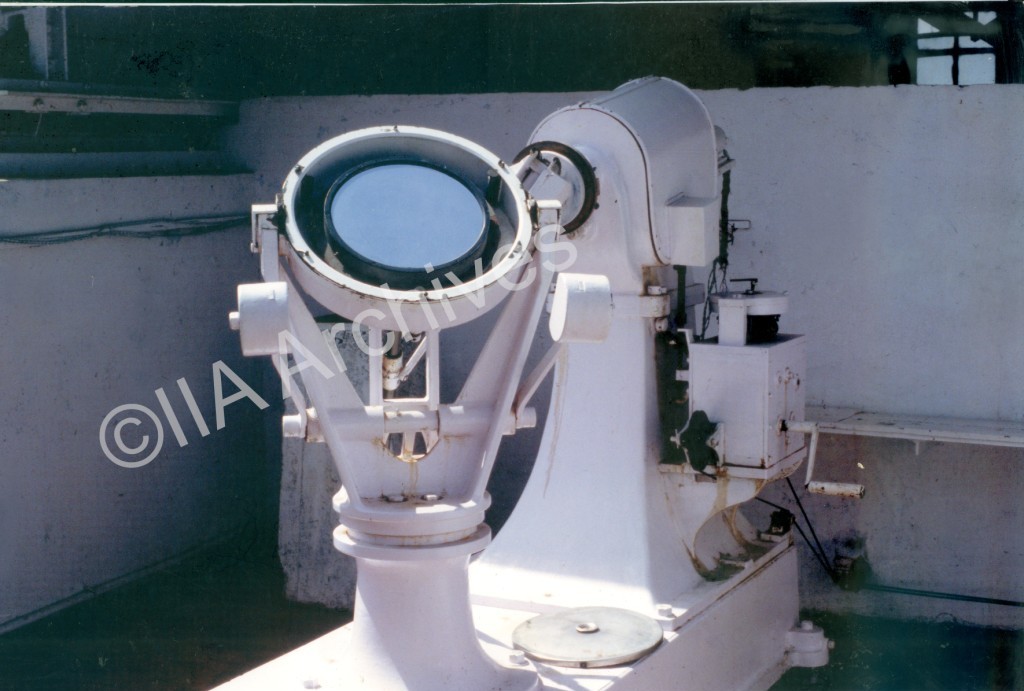 
12inch Siderostat at Kodaikanal-1986 | 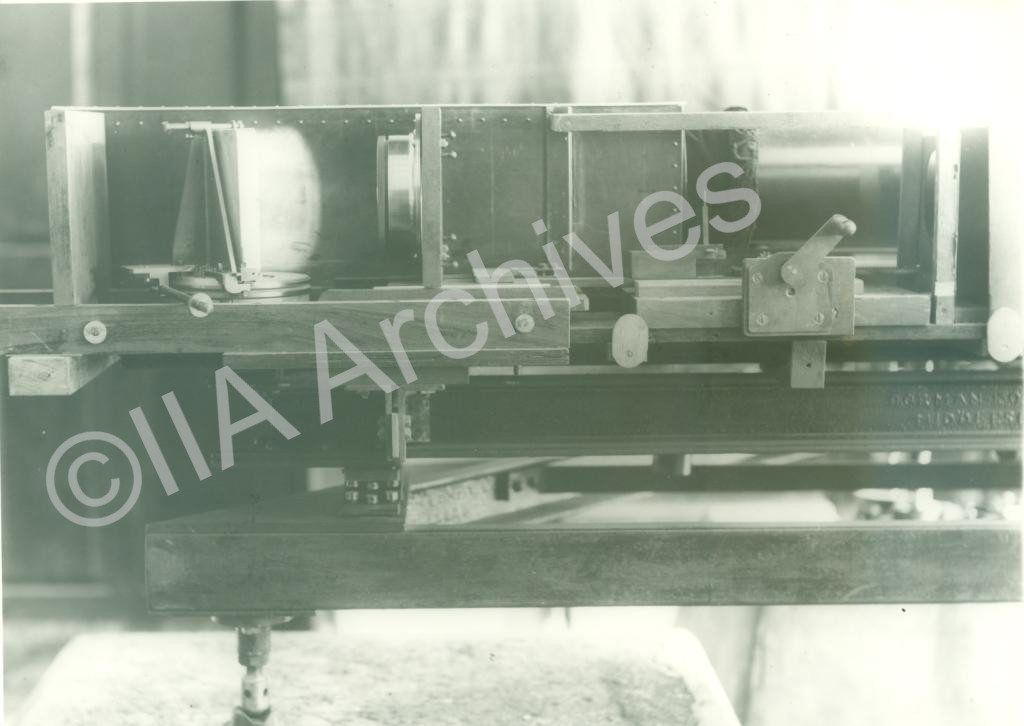 Grating and lens of the Auto-Collimating spectroheliograph-1911 Grating and lens of the Auto-Collimating spectroheliograph-1911 |